Misc
A Visual Guide to Human Emotion
A Visual Guide to Human Emotion
Despite vast differences in culture around the world, humanity’s DNA is 99.9% similar.
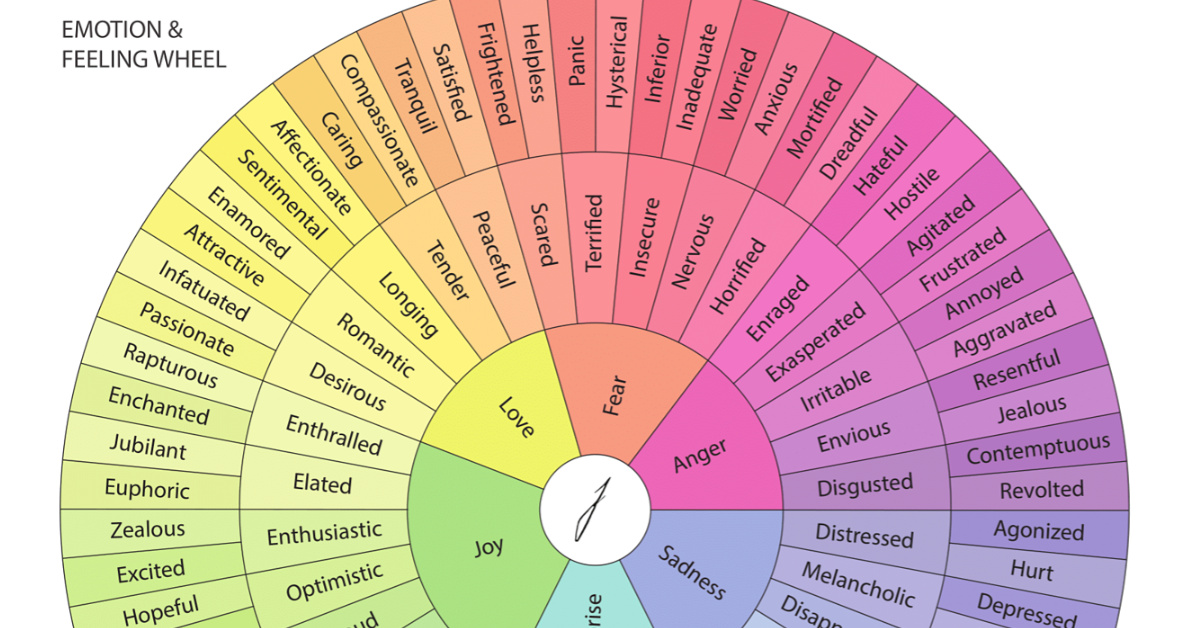
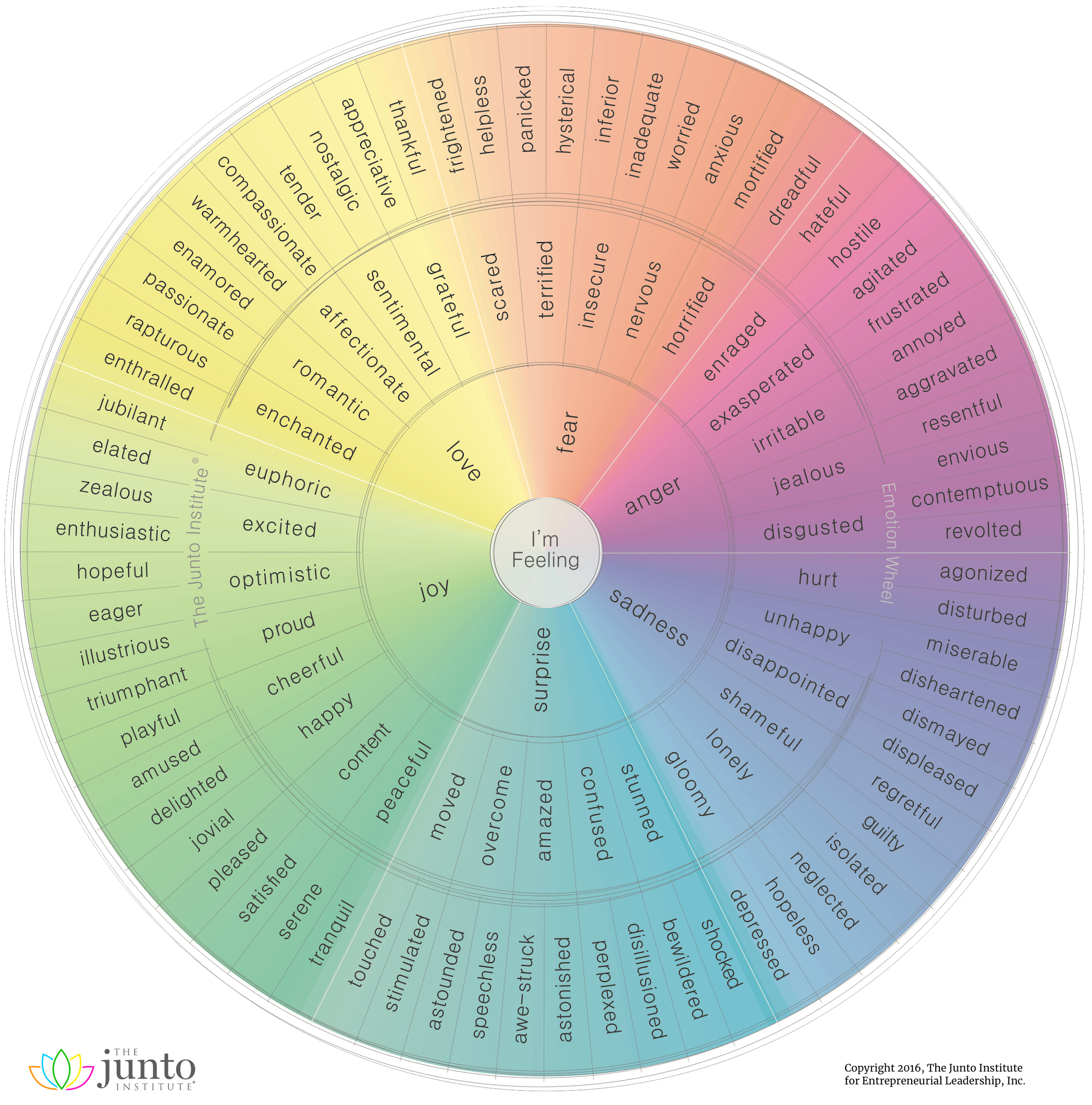
There are few attributes more central and universal to the human experience than our emotions. Of course, the broad spectrum of emotions we’re capable of experiencing can be difficult to articulate. That’s where this brilliant visualization by the Junto Institute comes in.
This circular visualization is the latest in an ongoing attempt to neatly categorize the full range of emotions in a logical way.
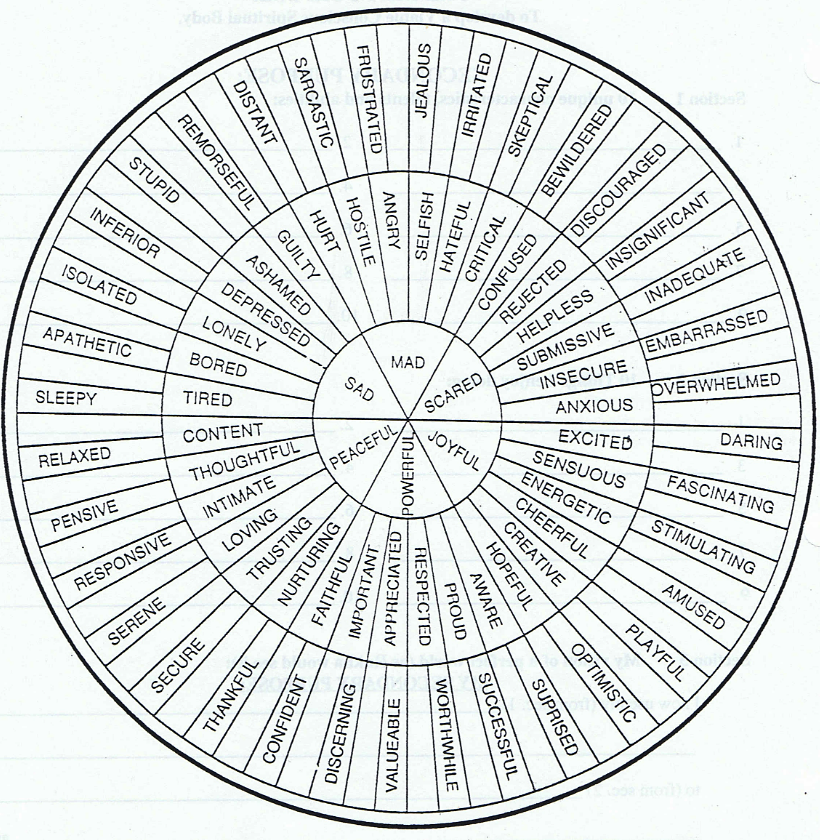
A Taxonomy of Human Emotion
Our understanding has come a long way since William James proposed four basic emotions – fear, grief, love, and rage—though these core emotions still form much of the foundation for current frameworks.
The wheel visualization above identifies six root emotions:
- Fear
- Anger
- Sadness
- Surprise
- Joy
- Love
From these six emotions, more nuanced descriptions emerge, such as jealousy as a subset of anger, and awe-struck as a subset of surprise. In total, there are 102 second- and third-order emotions listed on this emotion wheel.
Reinventing the Feeling Wheel
The concept of mapping the range of human emotions on a wheel picked up traction in the 1980s, and has evolved ever since.
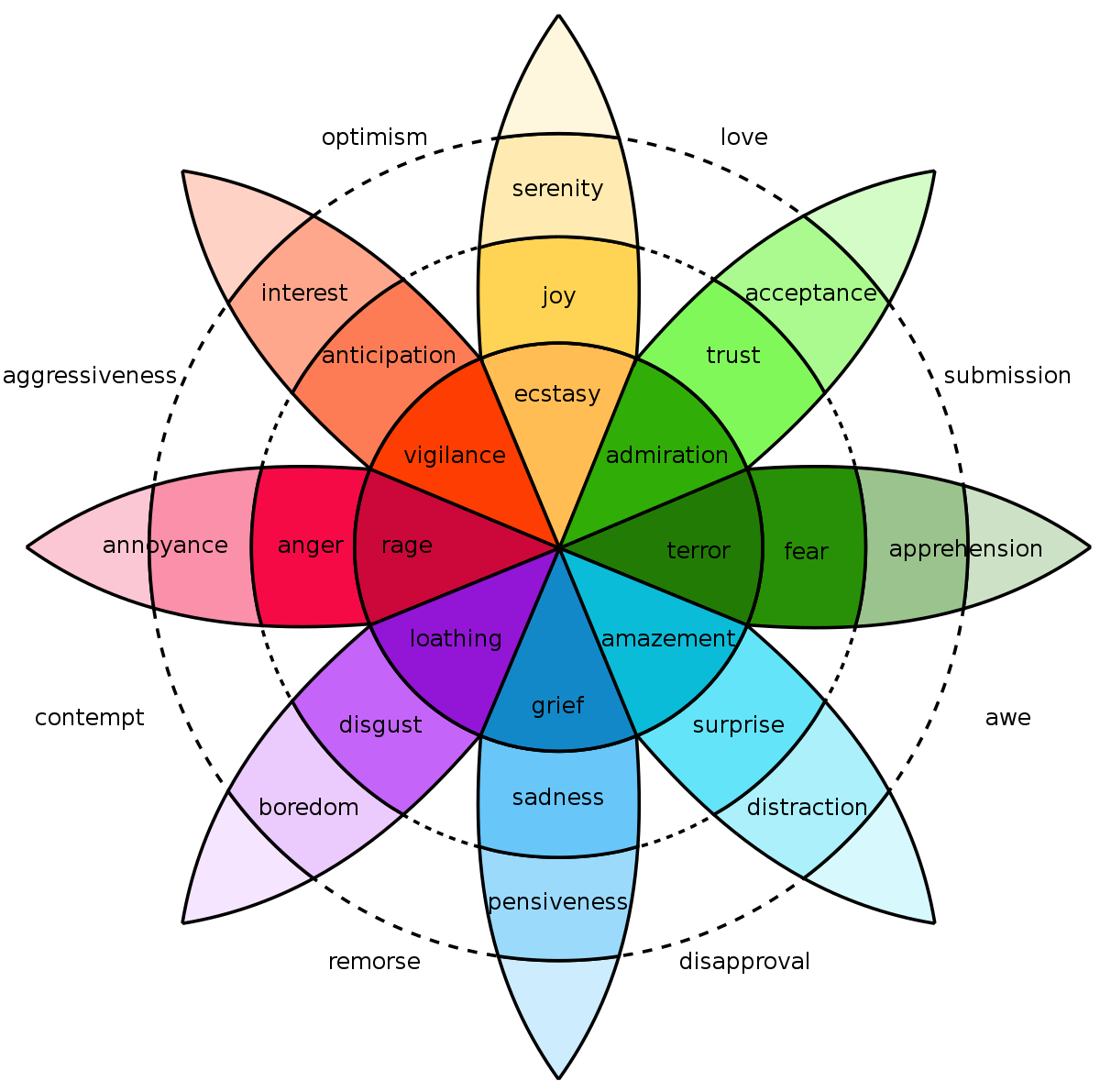
One of these original concepts was developed by American psychologist Robert Plutchik, who mapped eight primary emotions—anger, fear, sadness, disgust, surprise, anticipation, trust, and joy. These “high survival value” emotions were believed to be the most useful in keeping our ancient ancestors alive.
Another seminal graphic concept was developed by author Dr. Gloria Willcox. This version of the emotions wheel has spawned dozens of similar designs, as people continue to try to improve on the concept.
Further Exploration
The more we research human emotion, the more nuanced our understanding becomes in terms of how we react to the world around us.
Researchers at UC Berkeley used 2,185 short video clips to elicit emotions from study participants. Study participants rated the videos using 27 dimensions of self-reported emotional experience, and the results were mapped in an incredible interactive visualization. It is interesting to note that some video clips garnered a wide array of responses, while other clips elicit a near unanimous emotional response.
Here are some example videos and the distribution of responses:
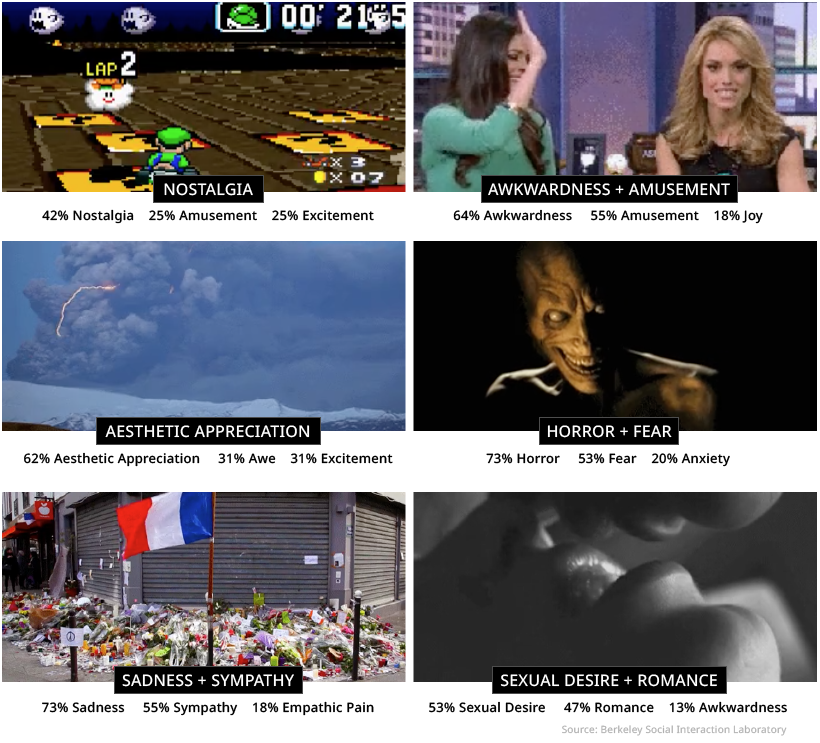
The data visualization clusters these types of videos together, giving us a unique perspective on how people respond to certain types of stimuli.
Much like emotion itself, our desire to understand and classify the world around us is powerful and uniquely human.
Automotive
How People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
Examining how people get around using cars, public transit, and walking or biking, and the regional differences in usage.
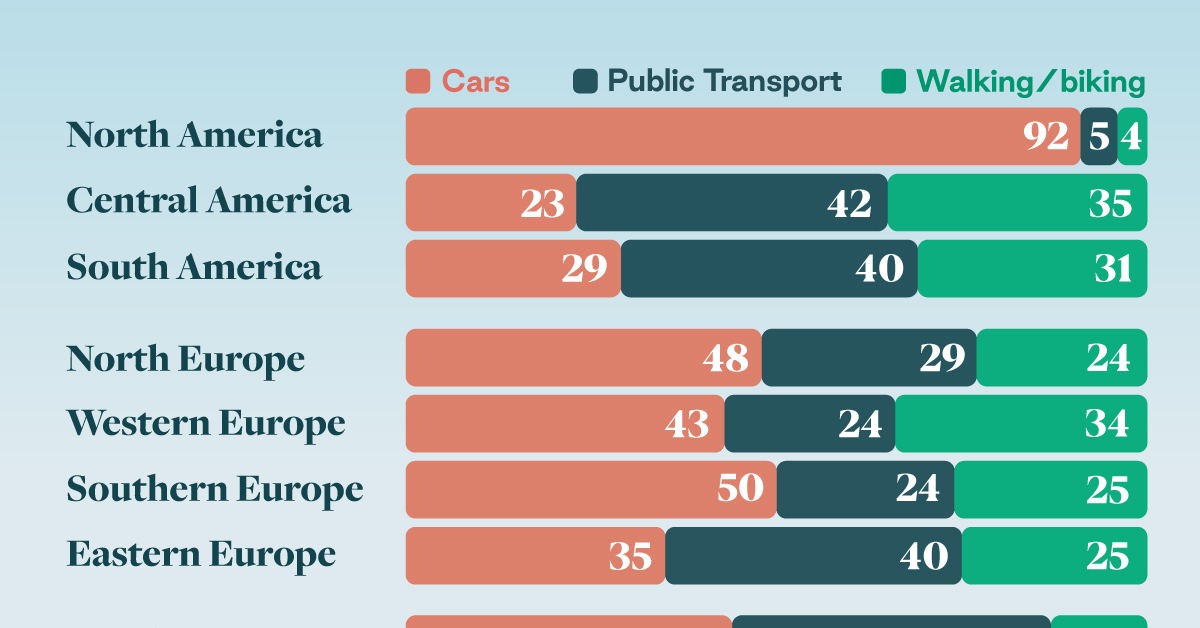
How People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
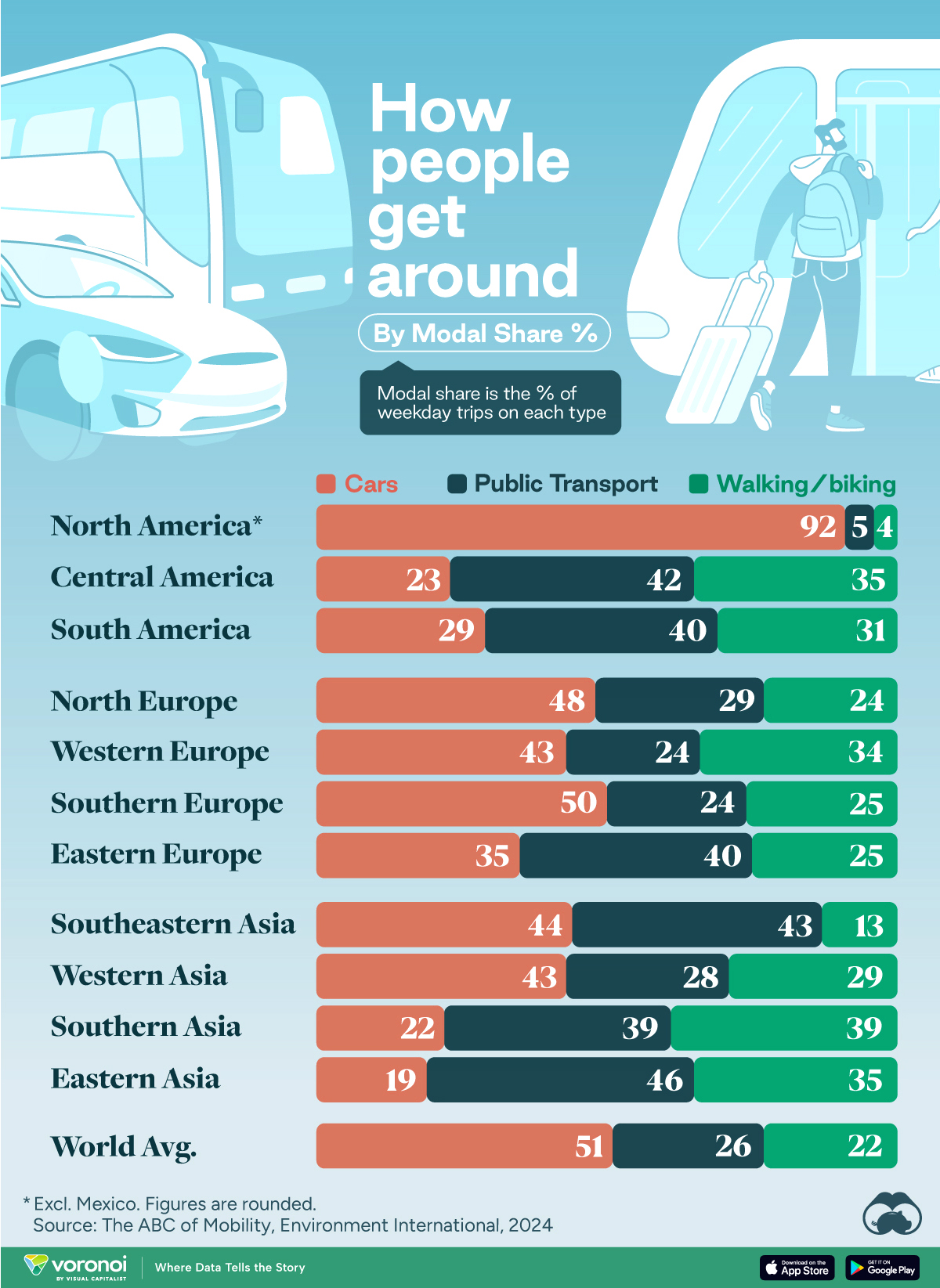
This chart highlights the popularity of different transportation types in the Americas, Europe, and Asia, calculated by modal share.
Data for this article and visualization is sourced from ‘The ABC of Mobility’, a research paper by Rafael Prieto-Curiel (Complexity Science Hub) and Juan P. Ospina (EAFIT University), accessed through ScienceDirect.
The authors gathered their modal share data through travel surveys, which focused on the primary mode of transportation a person employs for each weekday trip. Information from 800 cities across 61 countries was collected for this study.
North American Car Culture Contrasts with the Rest of the World
In the U.S. and Canada, people heavily rely on cars to get around, no matter the size of the city. There are a few exceptions of course, such as New York, Toronto, and smaller college towns across the United States.
| Region | 🚗 Cars | 🚌 Public Transport | 🚶 Walking/Biking |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America* | 92% | 5% | 4% |
| Central America | 23% | 42% | 35% |
| South America | 29% | 40% | 31% |
| Northern Europe | 48% | 29% | 24% |
| Western Europe | 43% | 24% | 34% |
| Southern Europe | 50% | 24% | 25% |
| Eastern Europe | 35% | 40% | 25% |
| Southeastern Asia | 44% | 43% | 13% |
| Western Asia | 43% | 28% | 29% |
| Southern Asia | 22% | 39% | 39% |
| Eastern Asia | 19% | 46% | 35% |
| World | 51% | 26% | 22% |
Note: *Excluding Mexico. Percentages are rounded.
As a result, North America’s share of public transport and active mobility (walking and biking) is the lowest amongst all surveyed regions by a significant amount.
On the other hand, public transport reigns supreme in South and Central America as well as Southern and Eastern Asia. It ties with cars in Southeastern Asia, and is eclipsed by cars in Western Asia.
As outlined in the paper, Europe sees more city-level differences in transport popularity.
For example, Utrecht, Netherlands prefers walking and biking. People in Paris and London like using their extensive transit systems. And in Manchester and Rome, roughly two out of three journeys are by car.
-
 Markets5 days ago
Markets5 days agoVisualizing Global Inflation Forecasts (2024-2026)
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoThe Carbon Footprint of Major Travel Methods
-

 United States2 weeks ago
United States2 weeks agoVisualizing the Most Common Pets in the U.S.
-

 Culture2 weeks ago
Culture2 weeks agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 voronoi1 week ago
voronoi1 week agoBest Visualizations of April on the Voronoi App
-

 Wealth1 week ago
Wealth1 week agoCharted: Which Country Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThe Top Private Equity Firms by Country
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoThe Best U.S. Companies to Work for According to LinkedIn